How Bioprinting Technology is Revolutionizing Tissue Engineering
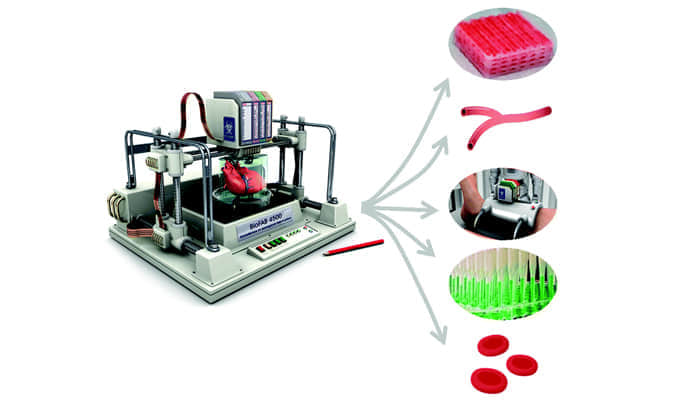
It is not a dream of the future anymore to incorporate Bioprinting into one’s life. It is an excellent kind of new technology that is greatly used in tissue engineering. Often referred to as a high-tech form of a pen that can produce living tissues and cells within a few steps, Bioprinting is transforming medical treatments, transplants, cloning techniques, or even the testing of drugs. Moving forward to the future of tissue engineering, this article outlines how Bioprinting has made a revolution in the field.
What is Bioprinting?

Bioprinting is a type of 3D printing that uses cells, growth factors, and biomaterials to create tissue-like structures. These structures mimic the properties of natural tissues, offering a new way to repair or replace damaged tissues in the body.
Types of Bioprinting:
- Inkjet Bioprinting: Uses a printer head to deposit cells in layers, creating a 3D structure.
- Extrusion Bioprinting: Involves the use of a syringe to push out cell-laden bio-ink to form tissues.
- Laser-Assisted Bioprinting: Employs laser beams to guide cells into place, allowing for high precision.
How Bioprinting Works

The process starts therefore with constructing a virtual image of the tissue or organ. This model helps the Bioprinter to lay down successively, a material called the bio-ink that has living cells and other products. Once printed, the structure is ‘cultured’ in order to facilitate the growth of cells and the formation of living tissue.
Use of Bioprinting in controlling and developing organs for transplant.

Tissue engineering is proving that Bioprinting is an enabler for new options. Here’s how:
Organ Transplants
Organ Shortage Solution: This scourge of shortage of organ donors has been at the forefront for several years now. Three potential advantages of using Bioprinting are manufacturing of organs from the patient’s cells eliminates the chance of rejection, and shortens the waiting list.
Tailor-Made Organs: With the help of bioprinting, one is in a position to fabricate organs in a way that suits a patient and thus is likely to enhance the efficiency of the operations that are carried out in relation to transplants.
Drug Testing and Development
Ethical Alternative: For this reason, Bioprinted tissues are something more ethical than animal testing yet they give accurate results.
Personalized Medicine: With the help for example Bioprinted tissues from the patient’s cells doctors are able to conduct track testing where the drugs are administered in a small dosage and the bad effects are minimized.
Regenerative Medicine
Skin Grafts and Wound Healing: Some of the one-of-a-kind applications of Bioprinting include the generation of skin substitutes in case of burns or critically damaged skin tissue.
Bone and Cartilage Repair: It can be for treatment in cases of injuries or diseases such as arthritis of bones and cartilage will be reconstructed by Bioprinted bone and cartilage.
Challenges Facing Bioprinting

While Bioprinting holds great promise, it’s not without its challenges:
Complexity of Human Tissues: The formation of such tissues as the heart or the liver is still rather a challenge though progress has been made. The spatial architecture of cells and blood vessels that interconnect them is hard to replicate.
Ethical Considerations: It becomes rather questionable when it comes to printing human tissues with special emphasis on whole organ generation.
Cost and Accessibility: The current Bioprinting devices are costly, thus making dispersion of its use into the market difficult.
The Future of Bioprinting in Tissue Engineering
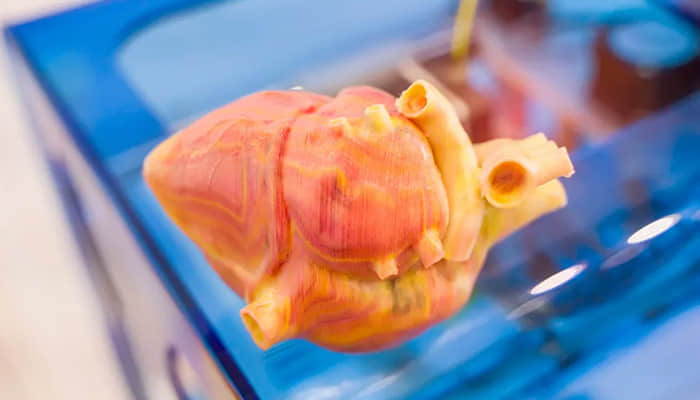
Despite the challenges, the future of Bioprinting in tissue engineering looks bright:
Advanced Tissue Models: Modern research focuses on designing increasingly higher-level tissues that would replicate human organs and would not require organ donors at all.
Regulatory Advances: With Bioprinting slowly transitioning to incorporating into everyday society, agencies are currently developing standards for use in healing processes.
Collaboration Across Fields: Bioprinting, can only work when there is close cooperation between biologists, engineers, and specialists in the medical field. Such an interdisciplinary approach is proving fruitful and getting us closer to that future in which tissue and organs are being bioprinted.
Conclusion
Bioprinting is one of the most revolutionary technologies in the field of tissue engineering. Its feature, which is the creation of living tissues and organs, holds enormous value for enhancing the quality of healthcare. Whether it be for addressing organ shortages, pushing the development of drugs, or introducing new ways towards regenerative medicine, Bioprinting will change the way through which the body is approached and healed. More innovations are on the horizon as technology advances, giving the world even more advancements of bioprinted organs than what has been mentioned above.






