The Importance of Gut Health: Your Microbiome and You
In recent years, gut health has emerged as a fascinating and vital area of scientific research, capturing the attention of experts across the globe. As studies continue to reveal the intricate connections between the gut and overall well-being, it is becoming clear that this system plays a far greater role in human health than previously understood.
At the heart of this discovery lies the gut microbiome—a bustling community of trillions of bacteria, fungi, and microorganisms that live within our digestive tract. Far from merely aiding digestion, these microscopic inhabitants are deeply intertwined with essential bodily functions, including mental health, immunity, and even the regulation of emotions. Often referred to as the “second brain,” the gut is not just a passive organ but an active player in maintaining our physical and emotional balance, making it a subject worthy of closer attention.
Understanding the Gut Microbiome: A Key to Better Health
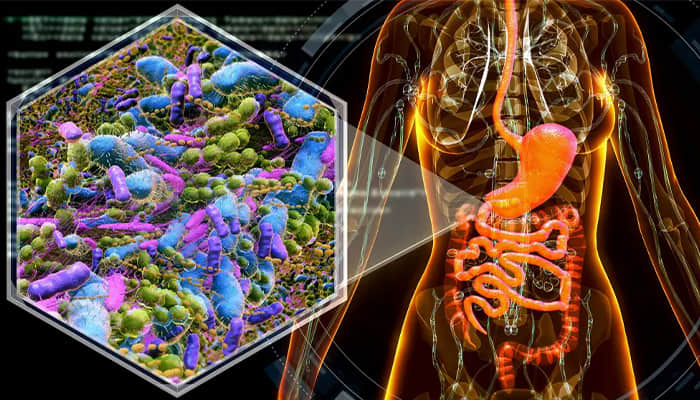
The gut microbiome refers to the community of microorganisms—bacteria, viruses, fungi, and more—living in the digestive tract. Remarkably, each person hosts around 200 different species of these microbes, creating a diverse ecosystem within their gut.
While some microorganisms can be harmful, many play vital roles in maintaining overall health. A well-balanced and diverse microbiome is essential for a healthy body. Studies suggest that a diverse array of gut bacteria may lower the risk of developing chronic conditions such as diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and psoriatic arthritis. This connection highlights that gut health is intricately linked to general well-being.
The Gut Microbiome’s Role in Your Health

The gut’s complex ecosystem significantly impacts overall health, and medical research has increasingly emphasized its importance. Over the years, studies have revealed connections between the gut microbiome and a wide range of health conditions, including:
- Mental health issues, such as anxiety and depression
- Autoimmune diseases, where the immune system attacks the body
- Endocrine disorders that affect hormones
- Digestive problems, including irritable bowel syndrome and inflammation
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Cancer
In addition, research suggests that greater diversity among gut bacteria often corresponds to better mental and physical health outcomes. Maintaining a balanced and varied microbiome is, therefore, not only beneficial but crucial for supporting overall well-being.
7 Warning Signs of Poor Gut Health
Modern lifestyle factors like stress, lack of sleep, consuming processed foods, and frequent antibiotic use can disrupt the gut’s natural balance. This imbalance can affect immune response, hormone regulation, weight, and overall health. If your gut is unhealthy, you may experience these seven common signs:
- Digestive Discomfort
Issues like gas, bloating, constipation, diarrhea, or heartburn could indicate a gut imbalance. A healthy gut processes food efficiently and eliminates waste without trouble.
- Diet High in Sugar and Processed Foods
Overeating sugary and processed foods can reduce the number of beneficial bacteria in your gut, causing an imbalance. This can lead to inflammation, which has been linked to conditions like cancer and chronic diseases.
- Unexpected Weight Changes
Unexplained weight gain or loss may stem from poor gut health. Imbalances can disrupt nutrient absorption, blood sugar regulation, and fat storage. For example, weight loss might be tied to nutrient malabsorption, while weight gain could result from inflammation or insulin resistance.
- Poor Sleep or Chronic Fatigue
Gut health impacts sleep quality. Imbalances in gut bacteria have been linked to disrupted sleep and persistent fatigue. This might be due to inflammation, metabolic issues, or even mental health factors.
- Skin Problems
Conditions like acne, eczema, or psoriasis could be connected to your gut. When your gut has fewer beneficial bacteria, it may trigger immune system issues that lead to skin irritation or inflammation.
- Weakened Immune System
The gut and immune system are closely connected. An unhealthy gut can increase inflammation in the body, potentially leading to autoimmune diseases, where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells.
- Food Sensitivities
Difficulty digesting certain foods, such as dairy or gluten, might signal an imbalanced gut. This can result in symptoms like bloating, gas, or stomach pain. Unlike allergies, food sensitivities are not immune reactions but can still cause significant discomfort.
7 Simple Ways to Support a Healthy Gut

Taking care of your gut doesn’t require drastic changes—small, consistent adjustments to your lifestyle and diet can make a big difference. Here are seven straightforward strategies to improve your gut health naturally.
1. Manage Stress Levels
Stress affects your entire body, including your digestive system. When you’re stressed, your body releases hormones that can disrupt gut function, potentially leading to discomfort and imbalance.
Try these stress-relief techniques:
- Practice mindfulness or meditation to calm your mind.
- Take daily walks to clear your head and stay active.
- Laugh often—watch a comedy or spend time with friends who make you smile.
- Engage in yoga or deep-breathing exercises to relax.
- Spend time with pets, which can lower stress levels naturally.
2. Prioritize Quality Sleep
Sleep and gut health are closely linked. Poor sleep can disrupt your gut, and an unhealthy gut can make it harder to get restful sleep. Aim for 7–8 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night to support your gut and overall health.
Tips for better sleep:
- Create a bedtime routine, such as reading or taking a warm bath.
- Limit screen time an hour before bed to avoid blue light exposure.
- Keep your bedroom dark, quiet, and cool for optimal sleep conditions.
3. Eat Mindfully
How you eat is just as important as what you eat. Chewing your food thoroughly and eating slowly gives your digestive system time to process food effectively, reducing bloating and discomfort.
Steps to practice mindful eating:
- Put down your fork between bites to pace yourself.
- Focus on the flavors and textures of your meal.
- Avoid distractions like scrolling on your phone or watching TV while eating.
- Keep Yourself Hydrate
Water plays a crucial role in keeping your digestive system running smoothly. Proper hydration can help prevent constipation and may even promote a more diverse and balanced gut microbiome.
To stay hydrated:
- Drink at least 8 glasses of water daily.
- Carry a reusable water bottle to make it easy to sip throughout the day.
- Add a slice of lemon or cucumber for flavor if plain water feels boring.
5. Include Prebiotics and Probiotics
Adding beneficial bacteria to your gut or supporting the growth of existing ones can enhance gut health.
- Prebiotics are fibers that feed good bacteria. Found in: garlic, onions, bananas, and asparagus.
- Probiotics are live bacteria that add to the microbiome. Found in: yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and supplements.
Before starting a supplement, consult a healthcare professional to find one that’s high-quality and suited to your needs.
6. Identify Food Sensitivities
Certain foods might irritate your gut, causing discomfort like bloating, gas, or nausea. Identifying and eliminating these triggers can improve digestion.
Steps to uncover sensitivities:
- Keep a food diary to track what you eat and how you feel afterward.
- Experiment with cutting out common triggers like dairy, gluten, or spicy foods one at a time.
- Gradually reintroduce these foods to see how your body reacts.
7. Eat for Gut Health
The foods you choose play a major role in gut health. A diet rich in fiber, plant-based foods, and healthy fats can help nourish your gut bacteria.
Incorporate these gut-friendly foods into your diet:
- Fiber-rich foods like beans, lentils, and whole grains.
- Polyphenol-packed items such as berries, nuts, and green tea.
- Fermented foods like kimchi, pickles, and miso for natural probiotics.
Limit processed foods and added sugars, as they can harm your gut balance over time.
Gut health is a cornerstone of overall well-being, influencing digestion, mental health, immunity, and more. By understanding the importance of the gut microbiome and making intentional lifestyle changes, you can improve not only your gut health but also your quality of life. Remember, small consistent steps—like incorporating probiotics, managing stress, and staying active—can lead to significant, lasting benefits. Start today and give your gut the care it deserves for a healthier, happier you.